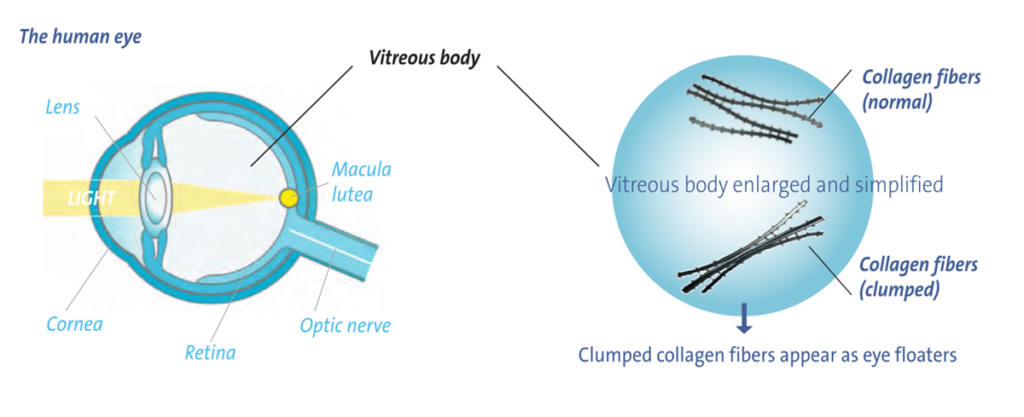
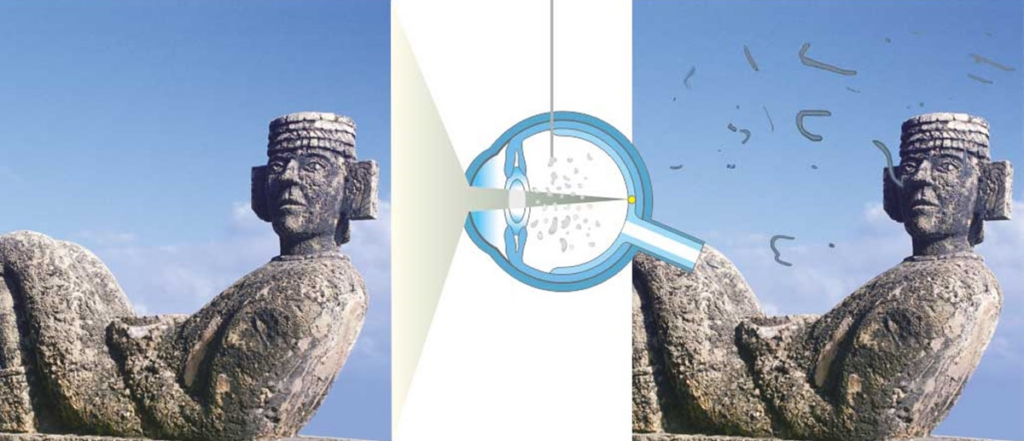
Natural treatment of floaters begins with a comprehensive understanding of their nature, the anatomy of a healthy vitreous body and the characteristics of its degeneration. Floaters are caused by the accumulation of collagen fibers in the vitreous humor, which cast shadows on the retina and manifest as dots, spots or thread-like structures.
Dive into this article for a quick primer on floaters and natural ways to counteract and overcome them. You can easily access specific sections by clicking on the table of contents on the left.
Degeneration of the Vitreous Body
The vitreous is composed of 98% water and macromolecules, forming a transparent, homogeneous gel that adheres to the retina. Its primary molecules include collagen fibrils and hyaluronic acid, which contributes to the gel-like consistency of the vitreous humor and aids in maintaining the structural integrity of the eye.
The homogeneity of the vitreous body is essential for clear vision, but it diminishes with age as well as independently of it.
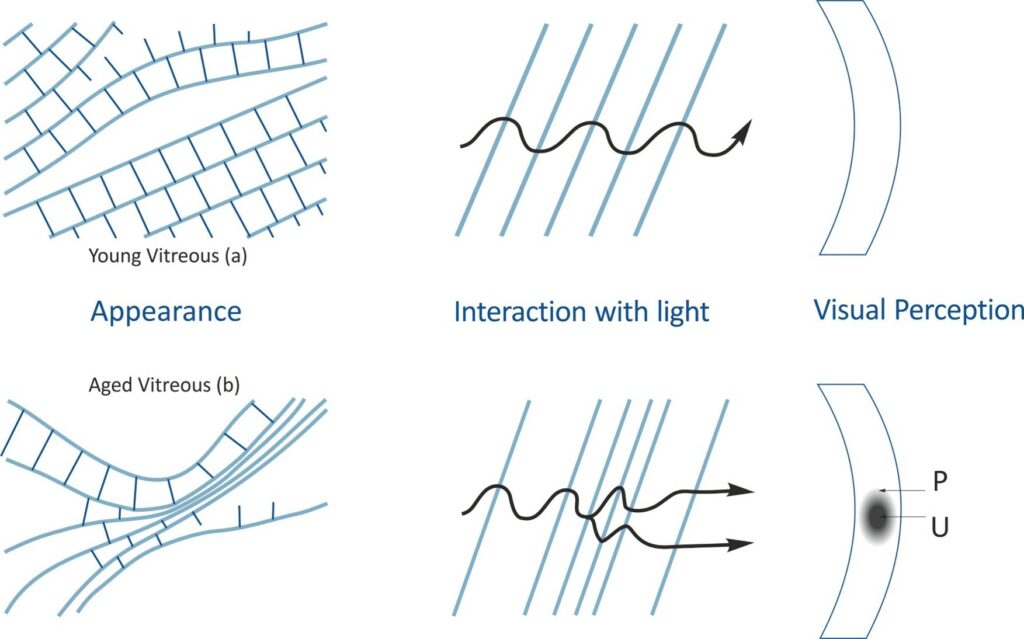
- Liquefaction (synchysis) of the vitreous body leads to the formation of small gaps or cysts. This happens because hyaluronic acid separates from collagen molecules, while collagen fibers clump together. Scientists call this aggregation of collagen fibers syneresis. This process results in areas with high concentration of aggregated collagen fibers and regions without fibers containing liquefied gel.
- The connection between the retina and the vitreous body weakens. As a result, the vitreous body can eventually detach from the optic nerve and the surface of the retina, a condition known as posterior vitreous detachment. Sometimes, a so called “Weiss ring” forms from tissue near the optic nerve that remains attached to the back part of the vitreous body.
Neither the process of clumping collagen fibers nor the formation of a Weiss ring is typically noticed by the person affected, but they can cause light to scatter as well as create shadowy patterns on the retina, leading to what scientists call entoptic images. These images might look like gray lines, circles, worm-like shapes, or nodules that move around when the eyes or head move.
Back to a Healthy Vitreous Body
In its healthy state, the vitreous body maintains a well-balanced network of loosely arranged parallel collagen fibers, allowing light to pass through uninterrupted. . The healthy vitreous of an adult exhibits notably high concentrations of micronutrients, including:
- vitamin C
- zinc
- l-lysine
In addition to these micronutrients, dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC), a potent antioxidant and a metabolite of proanthocyanidin, has been discovered in the human vitreous. This finding underscores the importance of combating oxidative stress in the eye.
- Proanthocyanidins has been shown to inhibit protein glycation.
- Hesperidin regulates oxidative stress and reduces the level of inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting the formation of advanced glycation end products. Therefore it could help prevent collagen aggregation.
The listed micronutrients form the vitreous body’s unique protective mechanism against oxidative stress and collagen glycation. Providing the eye with naturally occurring micronutrients (vitamin C and zinc) and other micronutrients can help reactivate this mechanism, minimizing or even preventing collagen fibers from clumping.
Clinical Trial: In a groundbreaking clinical trial, participants suffering from symptomatic vitreous floaters were administered a daily supplement (VitroCap®N) containing 125 mg of l-lysine, 5 mg of zinc, 40 mg of vitamin C, 25 mg of proanthocyanidins and 60 mg of hesperidin for a duration of 6 months. The outcomes were nothing short of remarkable, revealing that supplementation presents a low-risk yet remarkably effective method for alleviating floaters. Find out more under the section CLINICAL TRIALS.
Natural supplementation of the vitreous
Vitamin C
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin plays a crucial role in supporting various physiological functions in the body, including collagen synthesis, immune function, and antioxidant defense. When it comes to reducing floaters in the eye naturally, Vitamin C helps counter intraocular oxidative stress by consuming reactive oxygen species and free radicals released at the vitreoretinal interface in an ascorbate-dependent manner.

Foods rich in Vitamin C include:
- Papaya
- Pineapple
- Mango
- Melons (Cantaloupe and Watermelon)
- Tomatoes
- Bell peppers (Red and Yellow)
- Leafy greens (Kale, Spinach, Broccoli)
- Brussels sprouts
- Cabbage
- Winter squash
- Sweet potatoes
When consuming foods rich in vitamin C, it’s important to consider factors that can affect its absorption and utilization by the body. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Cooking method: Vitamin C is sensitive to heat and can be easily destroyed during cooking. Opt for cooking methods such as steaming or microwaving, which can help retain more of the vitamin compared to boiling or frying.
- Storage and preparation: Proper storage and handling of fruits and vegetables can help maintain their vitamin C content. Store them in a cool, dark place and avoid prolonged exposure to air, light, and heat. Additionally, minimize the amount of time fruits and vegetables are cut or peeled before consumption to reduce nutrient loss.
- Variety of sources: Consuming a diverse range of fruits and vegetables ensures a broader spectrum of nutrients, including vitamin C. Aim for a colorful plate with a mix of different fruits and vegetables to maximize your intake of this essential vitamin.
- Bioavailability: While vitamin C from natural food sources is generally well absorbed by the body, certain factors can affect its bioavailability. For example, the presence of dietary fiber and other compounds in fruits and vegetables may slow down the absorption of vitamin C. However, this is generally not a concern for individuals with a balanced diet.
- Individual factors: Factors such as age, health status, and genetics can influence how efficiently the body absorbs and utilizes vitamin C. Individuals with certain health conditions or dietary restrictions may benefit from consulting a healthcare professional to determine their specific vitamin C needs.
Zinc
Zinc is renowned for its potent antioxidative properties, which play a crucial role in maintaining ocular health. As an essential cofactor for various antioxidant enzymes, zinc effectively scavenges harmful free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative stress within the eye. By neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and preventing oxidative damage to ocular tissues, zinc helps preserve visual function and mitigates the risk of age-related eye conditions.
In addition to its antioxidative properties, zinc exhibits significant antiglycation properties that are beneficial for ocular health. Glycation is a process where sugars react with proteins, forming advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) that contribute to tissue damage and inflammation. Zinc interferes with glycation reactions, inhibiting the formation of AGEs and protecting ocular tissues from damage. By preventing glycoxidation and mitigating the accumulation of AGEs, zinc helps maintain the structural integrity of the eye and supports optimal visual function.
Zinc is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in numerous physiological processes within the body, including immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis. When it comes to naturally addressing eye floaters, zinc is instrumental in supporting ocular health by stimulating the synthesis of metallothionein, a metal-binding protein that protects tissues from glycoxidation—a mechanism associated with vitreous degeneration.
The European Food Safety Agency (EFSA) has recognized zinc’s significance, granting it a health claim for its role in maintaining normal vision.

Foods rich in zinc include:
- Beef
- Chicken
- Turkey
- Fish (such as salmon, tuna, and trout)
- Dairy products (including milk, cheese, and yogurt)
- Eggs
- Legumes (such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas)
- Nuts and seeds (like almonds, cashews, and pumpkin seeds)
- Whole grains (such as wheat germ and quinoa)
- Fortified cereals
L-lysine
L-lysine is an essential amino acid, meaning the body cannot produce it on its own and must obtain it from dietary sources. It helps prevent collagen glycation and serves as a chemical chaperone. The distinction between L-lysine and Lysine lies in their specific chemical structures, with L-lysine referring to the biologically active form of the amino acid Lysine.

Foods rich in lysine include:
- Meat (particularly red meat like beef and lamb)
- Poultry (such as chicken and turkey)
- Fish (including cod, sardines, and salmon)
- Dairy products (such as cheese, milk, and yogurt)
- Eggs
- Soy products (like tofu and tempeh)
- Legumes (including beans, lentils, and peas)
- Quinoa
- Pumpkin seeds
- Spirulina
Including these foods into one’s diet can help ensure an adequate intake of lysine.
Proanthocyanidins
Proanthocyanidins, also known as condensed tannins, are a class of polyphenolic compounds found abundantly in various plant-based foods and beverages. They are known for their potent antioxidant properties and have been linked to numerous health benefits. Proanthocyanidins have been shown to inhibit protein glycation. This inhibitory effect can help prevent the cross-linking of collagen fibers in the vitreous humor, potentially reducing the formation or severity of eye floaters.

Foods rich in proanthocyanidins include:
- Grapes (especially grape seeds)
- Berries (blueberries, cranberries, blackberries)
- Cocoa
- Red wine
- Nuts (almonds, pecans, walnuts)
- Certain vegetables (onions, spinach, broccoli)
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help increase your intake of proanthocyanidins, contributing to their potential health benefits. However, specific amounts of proanthocyanidins in each food can vary, and it’s essential to consume a diverse range of proanthocyanidin-rich foods as part of a balanced diet. While red wine contains proanthocyanidins, it’s not advisable to rely on alcohol as a source for supplementation to support the reduction of eye floaters. Excessive alcohol consumption enhances oxidative stress.
Hesperidin
Hesperidin is a flavonoid found in citrus fruits like oranges and lemons. It acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells and tissues from damage caused by free radicals and oxidative stress. This inhibitory effect may help maintain the structural integrity of collagen fibers in the vitreous humor, potentially reducing the formation or severity of eye floaters. By protecting against oxidative stress and inhibiting the formation of clumped collagen fibres, hesperidin may support overall health and function of the vitreous body, which can contribute to improved visual clarity and reduced occurrence of floaters.

Foods rich in hesperidin include:
- Oranges
- Lemons
- Grapefruits
Incorporating these hesperidin-rich citrus fruits into your diet can help increase your intake of this flavonoid, potentially offering health benefits such as antioxidant protection and support against oxidative stress. However, it’s important to consume a balanced diet with a variety of nutrient-rich foods to maximize overall health and well-being.
Supplementation Strategies: Pills vs. Natural Diet
When it comes to reducing floaters in the eye naturally and avoiding risks posed by clinical treatments such as vitrectomy or vitreolysis, the Floater Intervention Study (FLIES) marks a groundbreaking clinical trial investigating the impact of targeted nutritional supplementation on vitreous floaters. Significant improvements were observed, with varying times of onset. The clinical trial was evaluated after 6 months of treatment, revealing a reduction in complaint scores in 67% of patients, a decrease in vitreous opacity density in 77%, and a notable enhancement in visual function (contrast sensitivity). These positive outcomes were achieved through supplementation with VitroCap®N, a supplement consisting of 125 mg of L-lysine, 40 mg of vitamin C, 26.3 mg of grape seed extract (25 mg proanthocyanidins) , 5 mg of zinc, and 100 mg of Citrus fruit extract ( 60 mg bioflavonoids as hesperidin).
The question remains: Is it necessary or advisable to take pills for supplementing the vitreous and curing floaters, or is a natural healthy diet the solution of choice? There are compelling reasons for both:
Advantages of a natural Diet

- Nutrient Diversity: A natural diet provides a wide range of nutrients beyond those found in supplements, including vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytonutrients. Consuming a diverse array of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins and healthy fats can promote overall health and well-being.
- Bioavailability: Nutrients obtained from natural food sources are often more bioavailable than those from supplements. This means that the body can absorb and utilize these nutrients more efficiently, maximizing their health benefits. Additionally, natural foods contain other compounds that may enhance nutrient absorption and utilization.
- Sustainability and Affordability: Relying on natural foods for nutrient intake can be more sustainable and sometimes more affordable in the long run compared to purchasing supplements regularly. But: Modern farming practices have significantly reduced the micronutrient content in fruits and vegetables, making it harder to obtain essential nutrients from diet alone. This means one might need to consume more, and often more expensive, organically grown food to effectively support the body, thus diminishing the cost argument in favor of a natural diet alone.
Advantages of Supplementation with Capsules
- Precision and Consistency: Capsules offer precise and consistent dosages of specific nutrients, ensuring that you receive the exact amounts recommended for eye health every time you take them. This consistency is crucial, especially when targeting specific eye conditions like vitreous floaters.
- Convenience: Pills provide a convenient and hassle-free way to supplement your diet with essential nutrients for eye health. With busy lifestyles, it can be challenging to ensure that you’re getting enough of these nutrients solely from natural food sources on a daily basis.
- Tested Formulation: The supplement tested in 5 clinical trials has a proven effect on addressing floaters, specifically with its tested formulation and high-quality ingredients. Opting for evidence-based supplementation offers assurance, backed by clear success stories from other patients.
Beyond Either-Or: Both approaches can be complementary
While a natural diet may offer the benefits of nutrient diversity, bioavailability, sustainability, and affordability, taking capsules provides precision, consistency, convenience, and a tested formulation. Rather than choosing one over the other, both approaches can be complementary. In light of the groundbreaking clinical trial showcasing the potential benefits of targeted nutritional supplementation in addressing symptomatic vitreous floaters, it can be considered worthwhile to explore incorporating the tested capsules into one’s routine (always in addition to a balanced nutrition). The emergence of imitations in the market following the clinical trials on VitroCap®N raises considerations about the efficacy and reliability of alternative options. Although these alternatives may promote similar ingredients, it’s important to note that the rigorous research was exclusively conducted on VitroCap®N. Please keep in mind that the effect is a question of concentration, formulation and duration of supplementation. Some providers of eye floater supplements lack substantiated evidence for the effectiveness of their specific products and hide this deficiency behind the success of original clinical trials. This fact merits consideration when selecting suitable supplementation.
Healthy lifestyle

In addition to considering dietary choices and supplementation, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, stress management techniques and adequate hydration can role in managing vitreous floaters naturally.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity not only promotes overall health but also enhances blood circulation, including to the eyes. Exercise can help maintain optimal eye health by ensuring adequate delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the eyes, which may play a role in managing vitreous floaters naturally.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can contribute to various health issues, including eye strain and discomfort. Incorporating stress management techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga can help alleviate stress and promote relaxation, thereby reducing the risk of developing eye-related problems.
- Adequate Hydration: Proper hydration is essential for maintaining the health and function of all bodily systems, including the eyes. Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day helps keep the eyes lubricated and hydrated, reducing the likelihood of dry eyes and associated discomfort. Adequate hydration may also support the natural detoxification process within the eyes, potentially aiding in the management of vitreous floaters.
- Screen Time: In today’s digital age, it’s challenging to avoid screens, especially for those whose professions require prolonged computer use. However, minimizing screen time and taking regular breaks can help alleviate eye strain. Adjusting screen settings, such as brightness and contrast, or utilizing eye-saver features available on some devices, can also reduce eye fatigue.
- Wear Sunglasses: Protecting your eyes from harmful UV light exposure is crucial for maintaining eye health. Wearing sunglasses when outdoors can shield your eyes from the sun’s UV rays and reduce the risk of developing eye conditions associated with excessive sun exposure.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for overall health and well-being, including eye health. Getting enough sleep allows your eyes to rest and recover from the strains and stresses of the day, promoting optimal visual function and reducing the likelihood of experiencing eye discomfort or fatigue.
Incorporating these lifestyle practices alongside dietary adjustments and supplementation can contribute to a holistic approach into managing vitreous degeneration naturally, supporting long-term.



